The DEM-AWE Route-to-Market Report offers the first comprehensive commercial roadmap for deploying Kite-powered Battery Energy Storage Systems (K-BESS) in Northwest Europe. Developed under the Interreg NWE-funded DEM-AWE project, the report provides a market-driven strategy to scale Airborne Wind Energy through a mobile, and off-grid solution designed to replace diesel generators.
K-BESS: Enabling clean power where the grid cannot reach
K-BESS integrates AWE with on-site battery storage to supply renewable electricity in temporary, remote, or hard-to-electrify environments. The system targets three high-impact, and underserved markets:
-
Infrastructure construction sites (e.g. highways, dykes, railways) with high energy needs, limited grid access, and increasing pressure to decarbonize.
-
Quarries, often located in rural areas with energy-intensive operations and regulatory drivers for electrification.
-
Islands, where grid connection is technically or economically unfeasible and diesel remains a primary energy source.

Market sizing and commercial forecast
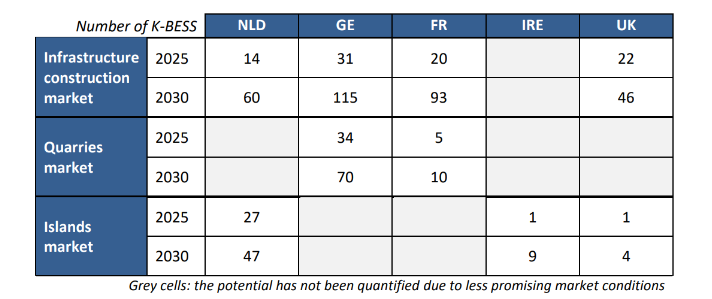
The study assesses five priority countries, Netherlands, Germany, France, Ireland, and the UK, using bottom-up data, stakeholder interviews, and GIS-based spatial analysis to estimate potential deployment of K-BESS. Key insights:
-
Construction sites represent the strongest early market: by 2030, the report foresees over 300 K-BESS units deployed across the five countries, with the Netherlands, Germany, and France leading.
-
Quarries in Germany and France could account for 80 additional units by 2030, driven by emission regulations and the shift to on-site renewables.
-
Islands, while smaller in number, present strategic opportunities, up to 60 units projected, especially aligned with the EU’s “Clean Energy for EU Islands” initiative.
Total realistic market potential by 2030 exceeds 450 units, with the Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCoE) of K-BESS systems expected to drop below diesel-based generation in several markets, especially where green energy incentives apply.
Strategic role in AWE commercialization
K-BESS plays a dual role: not only as an early revenue-generating product, but also as a technology validation platform and stakeholder engagement tool. It enables real-world performance testing, builds operator trust, and supports gradual scaling toward the long-term vision of grid-connected AWE farms.
The product leverages a 30kW AWE demonstrator by Kitepower, capable of charging a 400kWh battery in under 10 hours, and is currently being tested by partners like Dura Vermeer (Netherlands) and RWE (Ireland) in real construction and grid-constrained scenarios.
Commercial strategy and recommendations
To accelerate deployment, the report proposes a pragmatic route-to-market strategy:
-
Focus initial commercialization in remote infrastructure projects, where energy costs and grid limitations create a natural advantage for K-BESS.
-
Engage early adopters in construction and extractive industries to validate the model and generate visibility.
-
Pursue pilot projects and public procurement channels aligned with climate goals (e.g. NOx limits in the Netherlands, BEHG incentives in Germany, or “ZFE” zones in France).
-
Integrate AWE in broader renewable planning for resilient island energy systems.
A scalable path forward
K-BESS is more than a niche technology, it is a scalable gateway to unlock AWE’s full potential. As a mobile, and modular solution, it addresses immediate energy gaps while setting the stage for large-scale AWE integration into regional grids. The DEM-AWE consortium sees K-BESS as a commercially viable tool to accelerate the decarbonisation of off-grid Europe, and an important milestone in AWE’s journey from prototype to mainstream.